Generation Time Calculator – Complete Microbial Growth Guide
Generation time is a foundational concept in microbiology. It describes how quickly microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, fungi, and cultured cells reproduce under specific environmental conditions. This calculator uses real microbiology formulas to help you determine generation time, doubling time, and the number of generations that occurred during a growth experiment.
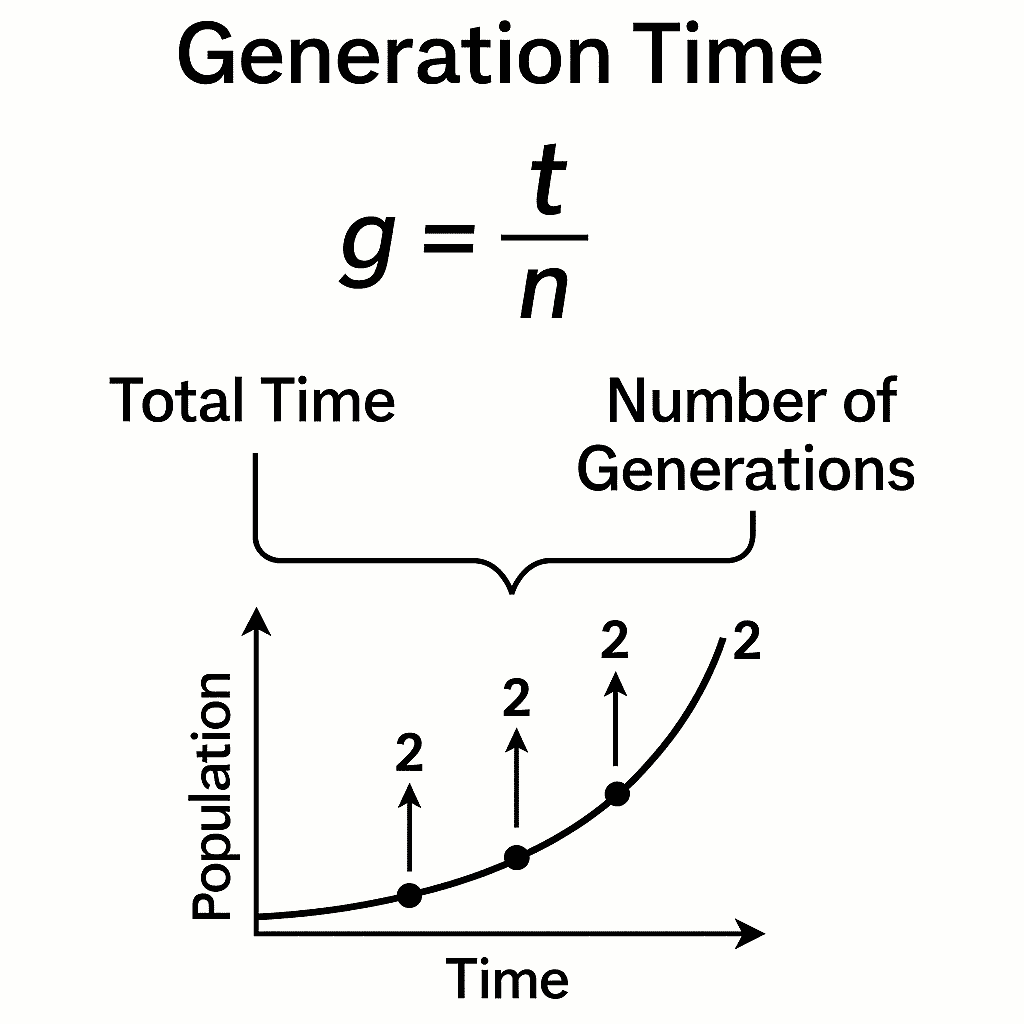
What Is Generation Time?
Generation time (g) refers to the average time required for a microbial population to double. During exponential (log) phase, microorganisms divide at a constant rate, making generation time easy to measure and compare.
- Short generation time → fast growth
- Long generation time → slow growth
Standard Microbiology Formulas
Microbiology relies on three core growth equations:
- Number of generations: n = (log N − log N₀) / log 2
- Generation time: g = t / n
- Population equation: N = N₀ × 2ⁿ
These formulas apply to bacteria, yeast, fungi, protozoa, and cell cultures exhibiting exponential growth.
Example Student Problem
Initial population (N₀): 5 × 10⁴
Final population (N): 8 × 10⁶
Total time (t): 120 minutes
Step 1 — Generations:
n = (log N − log N₀) / log 2 ≈ 4.32
Step 2 — Generation time:
g = 120 / 4.32 ≈ 27.8 minutes
Final Answer: Generation time ≈ 28 minutes.
Why Generation Time Matters
Generation time helps microbiology students and researchers understand:
- Bacterial growth curve behavior
- Food spoilage rates
- Bioreactor performance
- Infection doubling times
- Environmental microbial activity
Understanding Your Calculator Results
The calculator displays three important metrics:
- Number of generations (n): how many times the population doubled
- Generation time (g): average time per division
- Doubling time: identical to generation time under exponential growth
This makes the tool ideal for students, laboratory experiments, and quick data interpretation.
FAQ
Generation Time – Frequently Asked Questions
Answers to the most common questions about microbial growth calculations.
Generation time is the time required for a population of microorganisms to double under specific conditions.
It uses standard microbiology growth formulas to calculate number of generations, doubling time, or final population size.
You can use any time unit (minutes, hours, days) as long as it is consistent.
Yes. Any organism with exponential reproduction can be analyzed.
Yes. Enter initial and final populations to compute total generations.
Yes. Enter total time and number of generations.
Yes. Real growth depends on temperature, nutrients, oxygen, and pH, but formulas assume ideal exponential growth.
This uses the same formulas taught in microbiology and cell biology courses worldwide.
The tool uses n = (log N − log N0) / log 2 and g = t / n.
Yes. Using the exponential growth formula N = N0 × 2^n.